Smart Info About Can AC Charge DC Battery
.webp)
Is Your EV Battery Getting All The Energy You Pay For?
The AC/DC Battery Charging Conundrum
1. Understanding the Basics
Ever wondered if you can directly plug your wall outlet (AC) into your car battery (DC)? The short answer is no, not directly. It's like trying to fit a square peg in a round hole — you might force it, but you'll likely break something in the process. AC (Alternating Current) and DC (Direct Current) are different beasts, and batteries, by their nature, store energy in DC form. Think of AC as water flowing back and forth, while DC is a steady stream in one direction. Batteries are all about that steady stream.
Now, why is this important? Well, most of the electricity powering our homes and offices is AC. It's efficient for long-distance transmission. But many of our gadgets, including those that use batteries, need DC. That's where the magic of adapters and chargers comes in. They act as translators, converting AC to DC at the correct voltage for your device or battery.
Trying to directly charge a DC battery with AC would be like giving it a jolt of electricity that it can't handle. It could lead to overheating, damage to the battery, or even, in extreme cases, a fire. No bueno! So, respect the current; it's all about compatibility.
Think of it this way: you wouldn't fill your car's gas tank with diesel, would you? Same principle applies here. Different systems require different approaches. The right charger is key to keeping your batteries happy and healthy. So, always use the charger that's designed for your specific battery.
2. Delving Deeper
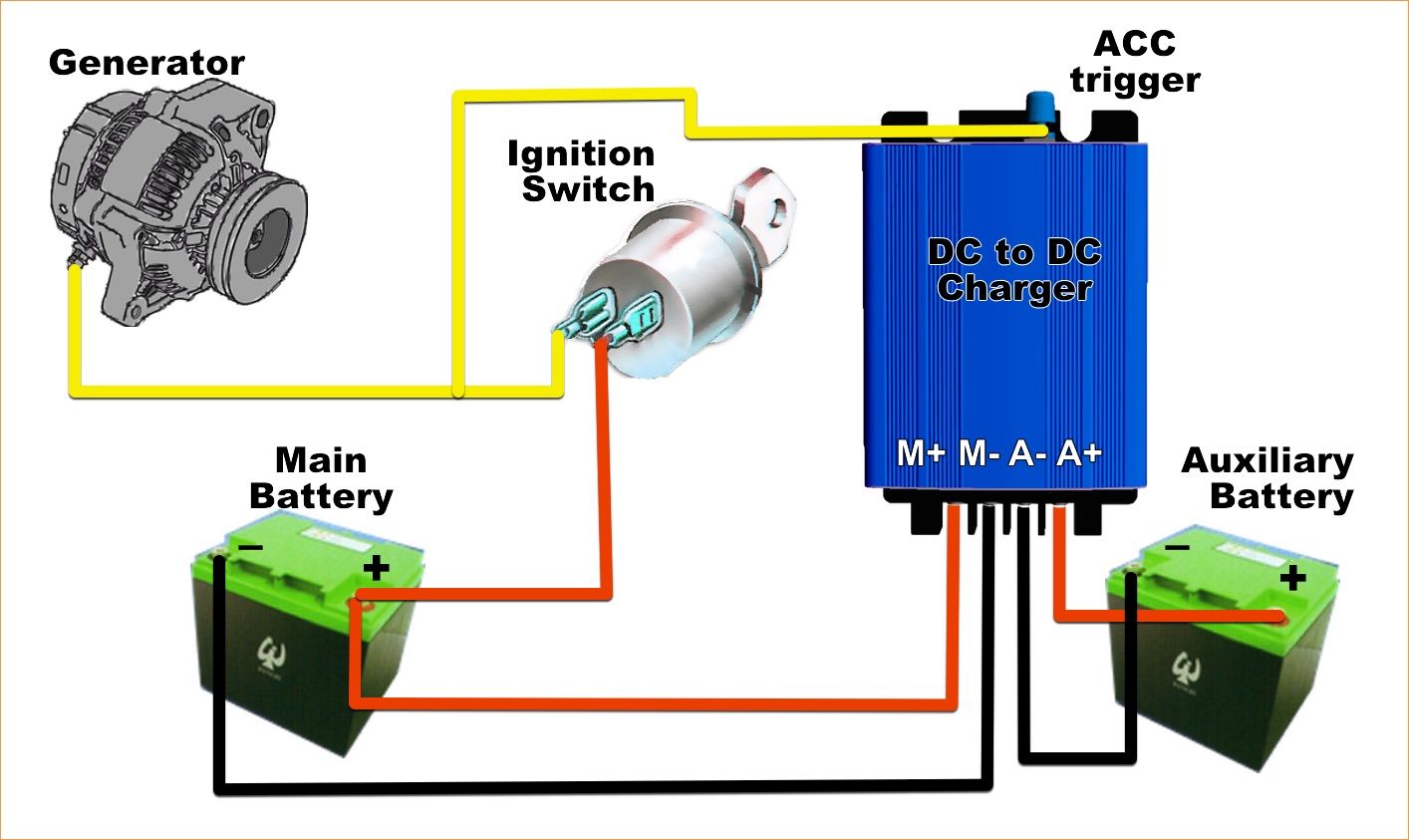
So, if you can't directly charge a DC battery with AC, how do you do it? Enter the heroes of our story: chargers and adapters. These little devices are crucial for bridging the gap between AC power and DC-hungry batteries. They're essentially power converters, taking the AC voltage from your wall outlet and transforming it into a stable DC voltage suitable for charging.
These chargers aren't just simple transformers; they're smart cookies. They regulate the voltage and current flowing into the battery, preventing overcharging and ensuring a safe and efficient charge. Modern chargers often have built-in safety features like short-circuit protection and thermal cutoffs, which are designed to prevent any mishaps.
The specific type of charger you need depends on the battery you're charging. A lithium-ion battery, for example, requires a different charging profile than a lead-acid battery. Using the wrong charger could damage the battery or shorten its lifespan. It's always a good idea to consult the battery's documentation or the device manufacturer's recommendations to ensure you're using the correct charger.
Think of the charger as a tailor, meticulously crafting the flow of electricity to perfectly suit the battery's needs. It's not just about converting AC to DC; it's about doing it safely and efficiently. So, next time you plug in your phone or laptop, take a moment to appreciate the clever engineering that's happening behind the scenes. It's what keeps your devices powered up and ready to go!
3. The Science Behind the Conversion
Let's dive a little deeper into the science of how chargers actually convert AC to DC. The process involves a few key components and stages. First, a transformer steps down the AC voltage from the wall outlet to a lower, more manageable level. Then, a rectifier converts the AC voltage to a pulsating DC voltage. This pulsating DC isn't smooth enough for charging batteries, so it passes through a filter, which smooths out the ripples and creates a more stable DC voltage.
The type of rectifier used can vary, but a common one is a bridge rectifier, which uses diodes to allow current to flow in only one direction. The filter typically consists of capacitors and inductors, which store and release energy to smooth out the voltage fluctuations. Think of the filter as a water reservoir that absorbs surges and provides a steady flow.
Modern chargers often use more sophisticated techniques, such as switched-mode power supplies (SMPS), which are more efficient and compact. SMPS use high-frequency switching to convert the voltage, allowing for smaller transformers and better regulation. They also tend to be lighter and more efficient than traditional linear power supplies.
The key takeaway here is that the conversion from AC to DC is not a simple process. It involves multiple stages and components, each playing a crucial role in ensuring a safe and efficient charge. This is why it's so important to use a quality charger that's designed for your specific battery. A poorly designed charger could introduce noise or instability into the DC voltage, which could damage the battery or reduce its lifespan.
4. DIY Adventures and Potential Pitfalls
While it's generally not advisable to mess with electricity without proper training, some adventurous souls might wonder about building their own AC to DC converter or modifying an existing one. While it's technically possible, it's fraught with potential dangers and should only be attempted by experienced electronics hobbyists who understand the risks involved.
One of the biggest dangers is electrocution. AC voltage from the wall outlet is potentially lethal, and even low-voltage DC can be dangerous if handled improperly. Another risk is fire. A poorly designed or constructed converter could overheat and ignite nearby materials. There's also the risk of damaging the battery you're trying to charge.
Even if you manage to build a functional converter, it's unlikely to be as efficient or reliable as a commercially available charger. Modern chargers are designed with safety and efficiency in mind, and they undergo rigorous testing to ensure they meet safety standards. A DIY converter might lack these safety features, making it a risky proposition.
So, while the idea of building your own AC to DC converter might sound appealing, it's generally not worth the risk. Unless you have extensive experience with electronics and a thorough understanding of the dangers involved, it's best to stick with commercially available chargers that are designed for your specific battery. Your safety (and your battery's well-being) will thank you.
5. FAQ
6. Frequently Asked Questions
Let's tackle some common questions about charging DC batteries with AC.
Q: Can I use a higher voltage charger than my battery requires?A: Nope, that's generally a bad idea. Using a charger with a higher voltage than your battery requires can damage the battery or even cause it to explode. Stick with the recommended voltage for optimal performance and safety.
Q: What happens if I use a lower voltage charger?A: A lower voltage charger might not be able to fully charge your battery, or it might take a very long time. It's generally not harmful, but it's also not very efficient. Use the correct voltage for the best results.
Q: Is it okay to leave my battery charging overnight?A: Modern chargers are designed to stop charging when the battery is full, preventing overcharging. However, it's still a good idea to unplug your charger once the battery is fully charged to conserve energy and extend the battery's lifespan. Leaving it plugged in constantly, even with a smart charger, can sometimes lead to a slight decrease in battery health over the long term.


AC Vs DC Charging What’s The Difference? 1C EV

Pros & Cons Of DC Charging And AC Joint