Cant Miss Takeaways Of Info About What Is Potential Energy For

GCSE Energy Elastic Potential Teaching Pack Resources
Unlocking the Secrets of Potential Energy
1. The Energy That's Just Waiting to Happen
Ever felt like you're just brimming with potential? Like you're coiled and ready to spring into action? Well, that's kinda what potential energy is like! It's the energy an object has because of its position or condition, just waiting for the chance to unleash itself. Think of it as stored energy, a reserve of power patiently waiting to be used. It's not doing anything yet, but it could.
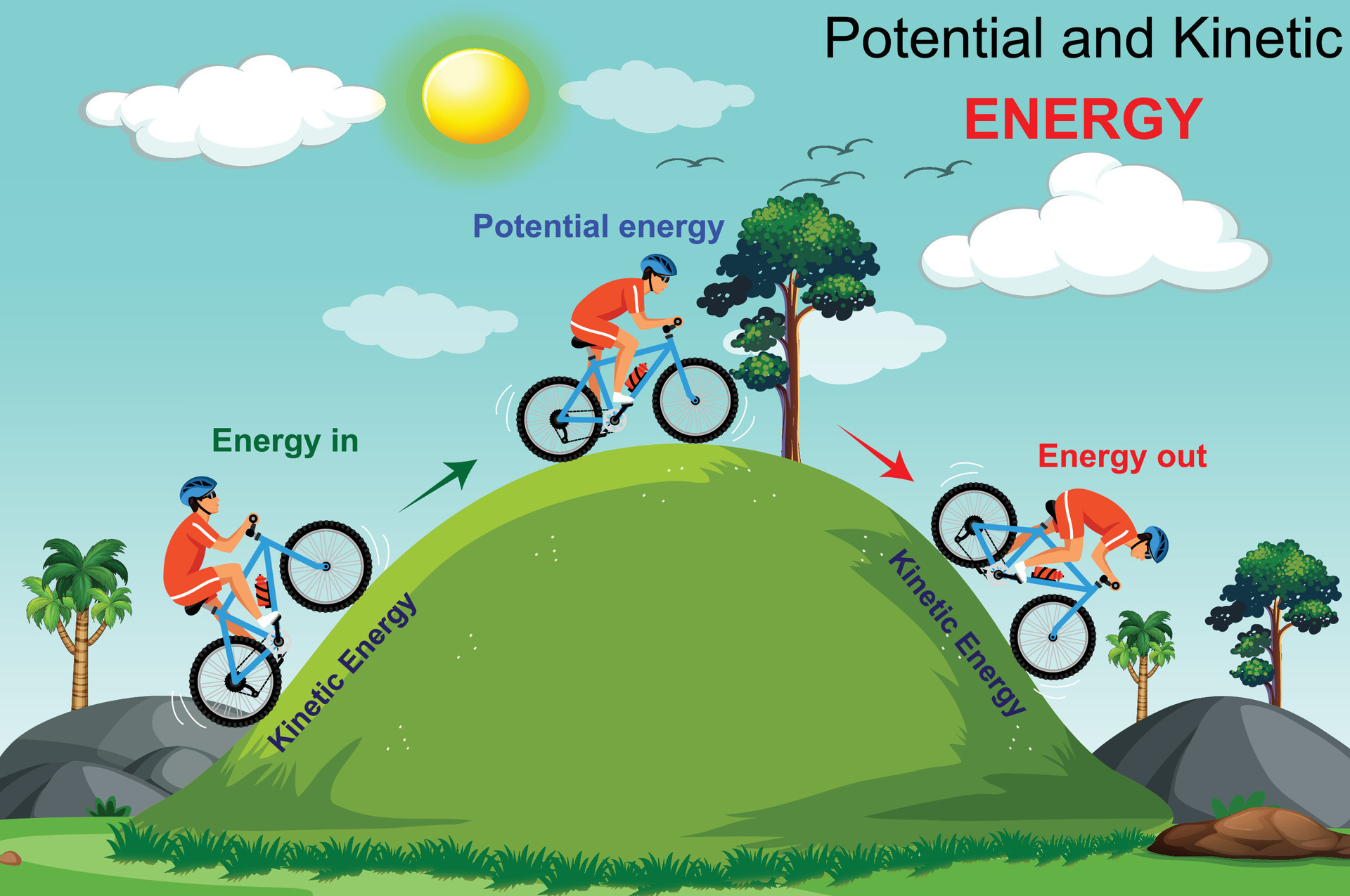
Imagine a rollercoaster car sitting at the very top of the first hill. That car isn't moving (yet!), but it's absolutely loaded with potential energy. Gravity is just itching to pull it down, converting that stored energy into thrilling, high-speed motion. The higher the hill, the more potential energy it has. It's like a delicious dessert sitting in the fridge. It's not satisfying your sweet tooth yet, but oh boy, the potential is there!
So, potential energy is basically the "what if" energy. What if that object falls? What if that spring is released? What if that rubber band snaps? The amount of potential energy depends on several things, like the object's mass, its height, and the forces acting upon it. Heavier things, higher places, and stronger forces generally mean more potential energy. Think of a bowling ball versus a tennis ball held at the same height. The bowling ball has way more potential to make a mess when it drops!
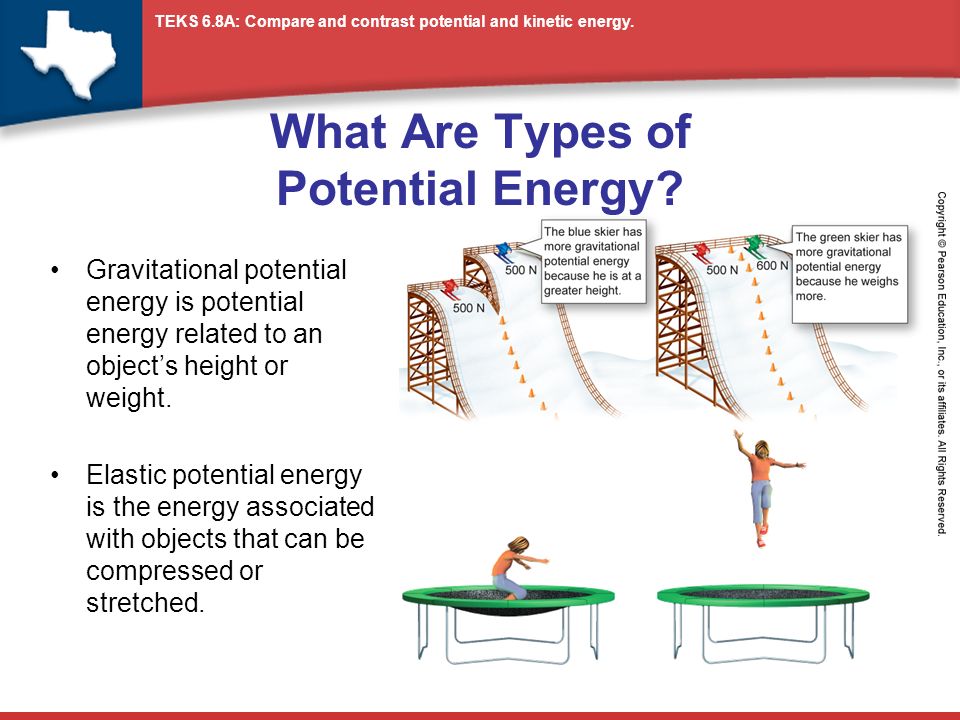
There are different kinds of potential energy too. We have gravitational potential energy, which depends on height, elastic potential energy, which depends on how much something is stretched or compressed (like a spring), and even chemical potential energy, which is stored in the bonds of molecules (like the energy in gasoline or a battery). It's all around us, just waiting to be unleashed!
Gravitational Potential Energy
2. Reaching New Heights of Understanding
Let's dive a bit deeper into gravitational potential energy, since it's one of the most common types we encounter. Gravitational potential energy is the energy an object has because of its position relative to a gravitational field (usually, good ol' Earth). The higher up something is, the more gravitational potential energy it possesses. It's all about that height difference, baby!
Think about an apple hanging from a tree. It's just chilling there, not doing much. But, because it's suspended high above the ground, it has a certain amount of gravitational potential energy. If the stem breaks, gravity will kick in, converting that potential energy into kinetic energy (the energy of motion) as the apple falls. Thud! Lunch is served (or at least, bruised).
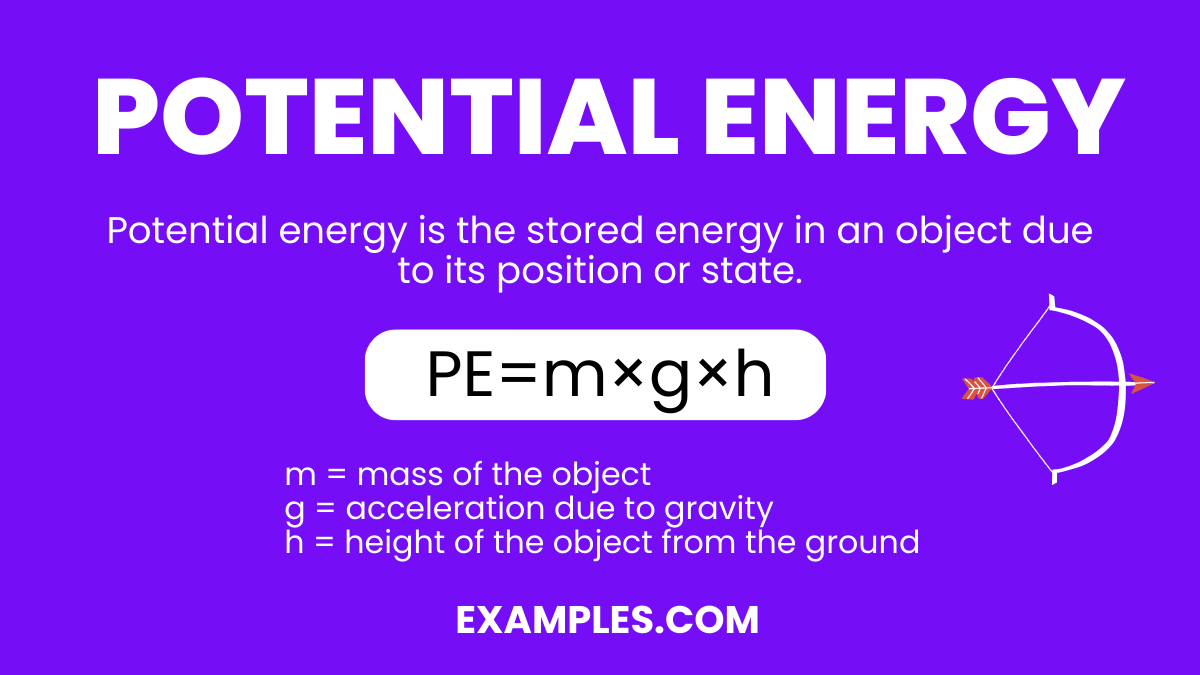
The formula for calculating gravitational potential energy is pretty straightforward: GPE = mgh, where 'm' is the mass of the object, 'g' is the acceleration due to gravity (approximately 9.8 m/s on Earth), and 'h' is the height above a reference point (usually the ground). So, if you know the mass of an object and how high it is, you can easily figure out how much potential energy it's packing. It's like a superpower, but for physics!
Gravitational potential energy is crucial in all sorts of scenarios. Hydroelectric dams use it to generate electricity, exploiting the height difference of water. Construction workers use it to power pile drivers, dropping heavy weights to hammer pilings into the ground. Even everyday activities, like walking up stairs, involve increasing your gravitational potential energy. So, next time you climb a hill, remember you're not just getting a workout, you're also increasing your potential!
What Are And Potential Energy? Ppt Download
Elastic Potential Energy
3. The Spring in Your Step, Explained!
Now let's talk about elastic potential energy. This is the energy stored in objects that are stretched or compressed, like springs, rubber bands, or even a trampoline. The more you stretch or compress these objects, the more elastic potential energy they store. It's like winding up a toy — the more you wind it, the more potential it has to zoom across the room.
Imagine stretching a rubber band between your fingers. As you pull it farther and farther, you're storing more and more elastic potential energy within its structure. When you release the rubber band, that stored energy is converted into kinetic energy, sending it flying (hopefully not into someone's eye!). The same principle applies to a spring in a pogo stick. When you jump on it, you compress the spring, storing energy that is then released to propel you upwards.
The amount of elastic potential energy stored in a spring is determined by Hooke's Law, which states that the force required to stretch or compress a spring is proportional to the distance it's stretched or compressed. The formula for elastic potential energy is: EPE = (1/2)kx, where 'k' is the spring constant (a measure of the spring's stiffness) and 'x' is the displacement from its equilibrium position. A stiffer spring (higher 'k' value) will store more energy for the same amount of displacement.
Elastic potential energy is utilized in countless devices and systems. Car suspensions rely on springs to absorb bumps and provide a smoother ride. Bows and arrows use elastic potential energy to launch projectiles. Even your mattress uses springs or foam to provide support and comfort while you sleep. So, elastic potential energy is all around us, making our lives a little more comfortable and a lot more fun!
And Potential Energy
Chemical Potential Energy
4. The Energy Hidden Within
Alright, let's shift gears and talk about chemical potential energy. This type of potential energy is stored in the chemical bonds of molecules. It's the energy that's released when these bonds are broken and new ones are formed during chemical reactions. This is the energy that fuels our cars, powers our homes, and even keeps our bodies running.
Think about gasoline. It's a complex mixture of hydrocarbons that contain a lot of chemical potential energy stored within their molecular bonds. When gasoline is burned in an engine, these bonds are broken, releasing energy in the form of heat and light. This energy is then used to push pistons and turn the wheels of your car. Similarly, food contains chemical potential energy that our bodies break down to provide us with the energy we need to move, think, and stay alive.
Batteries are another prime example of chemical potential energy storage. Inside a battery, chemical reactions occur that release electrons, creating an electric current. This current can then be used to power a flashlight, a cell phone, or even an electric car. The amount of chemical potential energy a battery can store depends on the types of chemicals it contains and the design of the battery.
Chemical potential energy is essential for modern life. It allows us to power our world, transport goods, and communicate with each other. However, it's also important to be mindful of the environmental impact of using fossil fuels, which release greenhouse gases when burned. That's why there's so much research and development focused on finding cleaner and more sustainable sources of chemical potential energy, like biofuels and hydrogen fuel cells.
.png)
Why Should You Care About Potential Energy?
5. The Real-World Applications
So, why should you care about potential energy? Well, understanding potential energy helps us understand how the world around us works. It's a fundamental concept in physics that explains everything from why things fall to how power plants generate electricity. It also allows us to design better technologies and create more efficient energy systems. Plus, it's just plain cool!
Knowing about potential energy can help you understand everyday phenomena. Why does a roller coaster go so fast? Why does a bow and arrow launch with such force? Why does a battery run out of power? The answers to all these questions lie in the principles of potential energy. It's like having a secret decoder ring for the universe!
Furthermore, understanding potential energy is crucial for developing new energy technologies. By understanding how to store and release energy efficiently, we can create better batteries, more efficient solar panels, and more sustainable transportation systems. It's all about harnessing the power of potential!
Ultimately, understanding potential energy allows us to appreciate the intricate and fascinating ways in which energy is stored and transformed in the world around us. It's a reminder that even when things appear to be still and quiet, there's often a hidden reservoir of power just waiting to be unleashed. So, keep exploring, keep questioning, and keep unlocking the secrets of potential energy!

Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
6. Your Potential Energy Questions Answered!
Here are some common questions that pop up when people start thinking about potential energy:
7. What's the difference between potential energy and kinetic energy?
Potential energy is stored energy waiting to be used, while kinetic energy is the energy of motion. Think of a stretched rubber band (potential) being released and flying through the air (kinetic). They are often converted into each other!
8. Can an object have both potential and kinetic energy at the same time?
Absolutely! Imagine that apple falling from the tree. As it falls, it's losing potential energy (because it's getting closer to the ground), but it's gaining kinetic energy (because it's speeding up). At any point during its fall, it has some amount of both.
9. Is potential energy always a good thing?
Not necessarily. While potential energy can be harnessed to do useful work, it can also be dangerous if not controlled. A large amount of potential energy suddenly released can cause damage or injury. Think of a landslide or an explosion.